Diabetes Complications: What Happens When Diabetes Is Not Well Managed?
By 2050, Singapore is expected to have around 1 million individuals with diabetes, owing to the rapidly ageing population.1
Elevated blood sugar (glucose) levels in the blood for a prolonged time can trigger a cascade of symptoms and lead to a range of complications that can affect nearly every organ in the body.2 The higher the blood sugar levels, the more the risk of developing complications.2
Diabetes complications
Complications due to diabetes can be divided into two major categories:2–4
1. Acute or short-term complications
These complications are serious, life-threatening, and may occur at any moment and could result in chronic or long-term conditions.
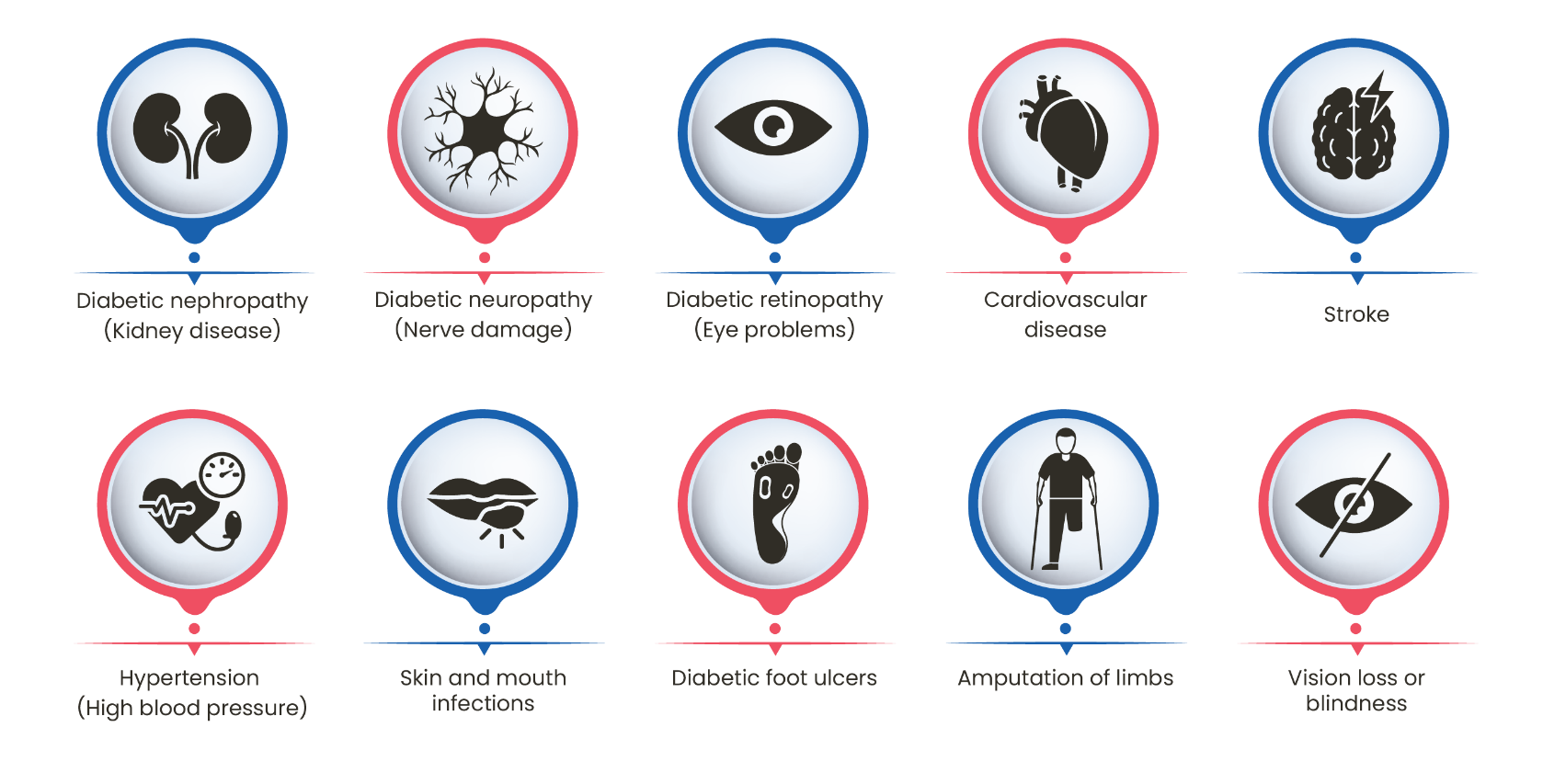
2. Chronic or long-term complications
These complications develop gradually over the years or decades and may cause significant harm or disability if left unchecked and untreated.

Preventing or delaying diabetes complications
The best way to prevent these complications is by following a healthy lifestyle, regularly monitoring blood sugar levels, taking medications as prescribed, and managing other risk factors, such as high cholesterol and high blood pressure.2,3
1. Remember your ABCs:3

 |
2. Exercise regularly: Exercise can improve the way your body uses insulin and can help prevent complications. | |
| 3. Eat a balanced diet: You can manage your blood sugar levels by eating a balanced, low-fat, and low-sugar diet. |  |
|
 |
4. Take your medications as prescribed: Consuming your medications as prescribed can help you keep your blood sugar levels within the target range. | |
| 5. Take care of your feet: Individuals with diabetes are more likely to experience foot problems. Complications can be avoided by taking good care of your feet and scheduling routine checkups with your doctor. |  |
|
 |
6. Do not skip your appointments: Regular doctor visits can aid in the early detection of any issues, allowing for effective diagnosis and treatment. | |
References
1. Tan KW, Dickens BS, Cook AR. Projected burden of type 2 diabetes mellitus-related complications in Singapore until 2050: A Bayesian evidence synthesis. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020;8(1):e000928.
2. Diabetes UK. Complications of diabetes. Available at: https://www.diabetes.org.uk/guide-to-diabetes/complications. Accessed on: 20 November 2022.
3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Put the Brakes on Diabetes Complications. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/library/features/prevent-complications.html. Accessed on: 20 November 2022.
4. Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG). Hyperglycaemia and hypoglycaemia in type 2 diabetes. National Library of Medicine Bookshelf. 2020. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279510/. Accessed on: 01 December 2022.
Article contributed by Frontier Healthcare Clinical Content Team
About Frontier Healthcare Group
Frontier Healthcare (as part of the Qualitas Primary Care Division) runs 18 GP clinics, 2 Family Medicine Clinics (Clementi and MacPherson) and has 37 affiliated GP clinics under its Frontier Primary Care Network Program. Frontier Healthcare supports national schemes such as the Community Health Assist Scheme (Pioneer, Merdeka, CHAS Green, CHAS Orange, CHAS Blue), Baby Bonus, Healthier SG, MBS@Gov etc, as well as partnerships with major Insurers, Corporates and TPA partners to bring quality and affordable healthcare closer to the community.




