Urinary Tract Infections
Understanding Urinary Tract Infections
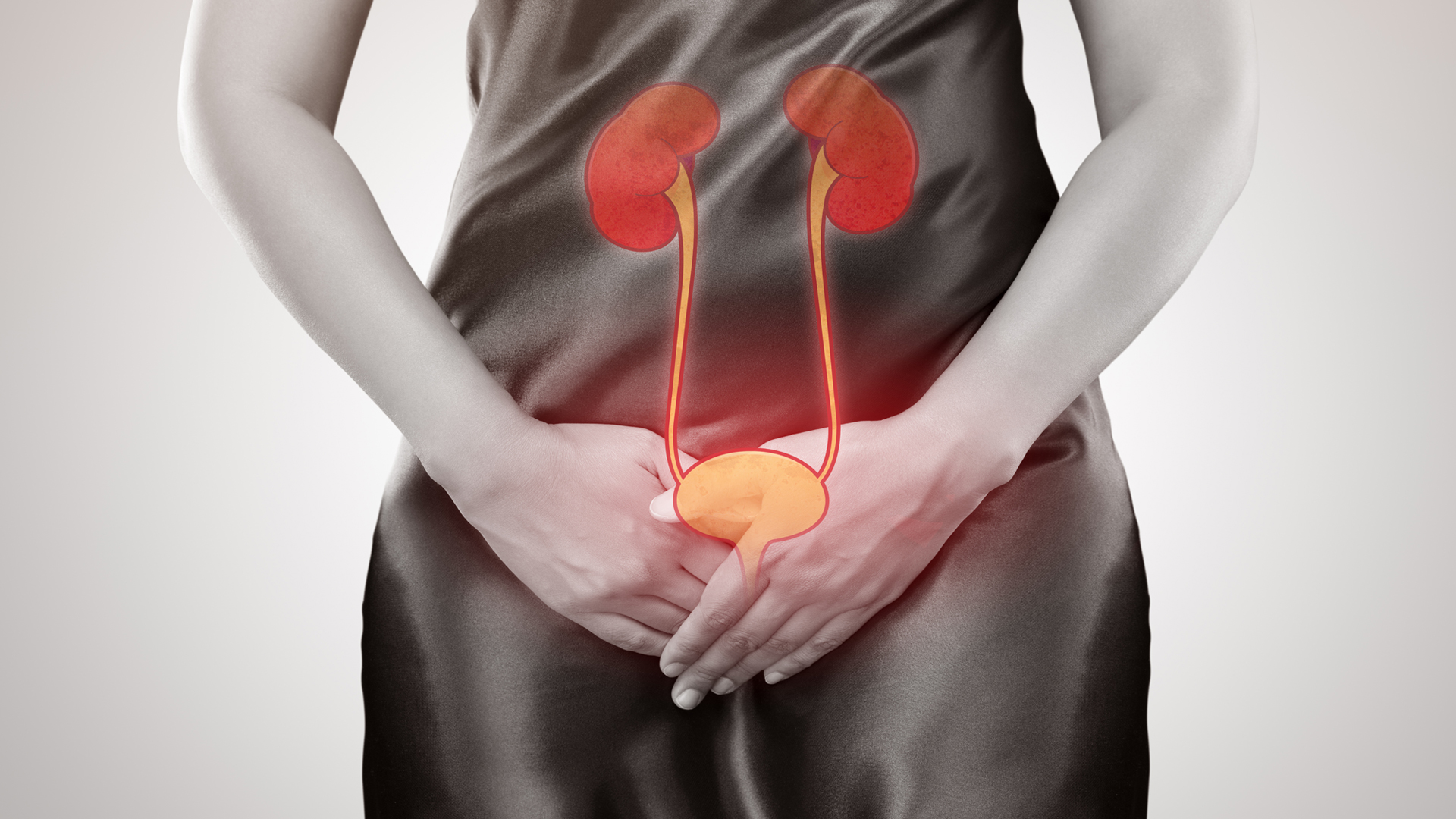
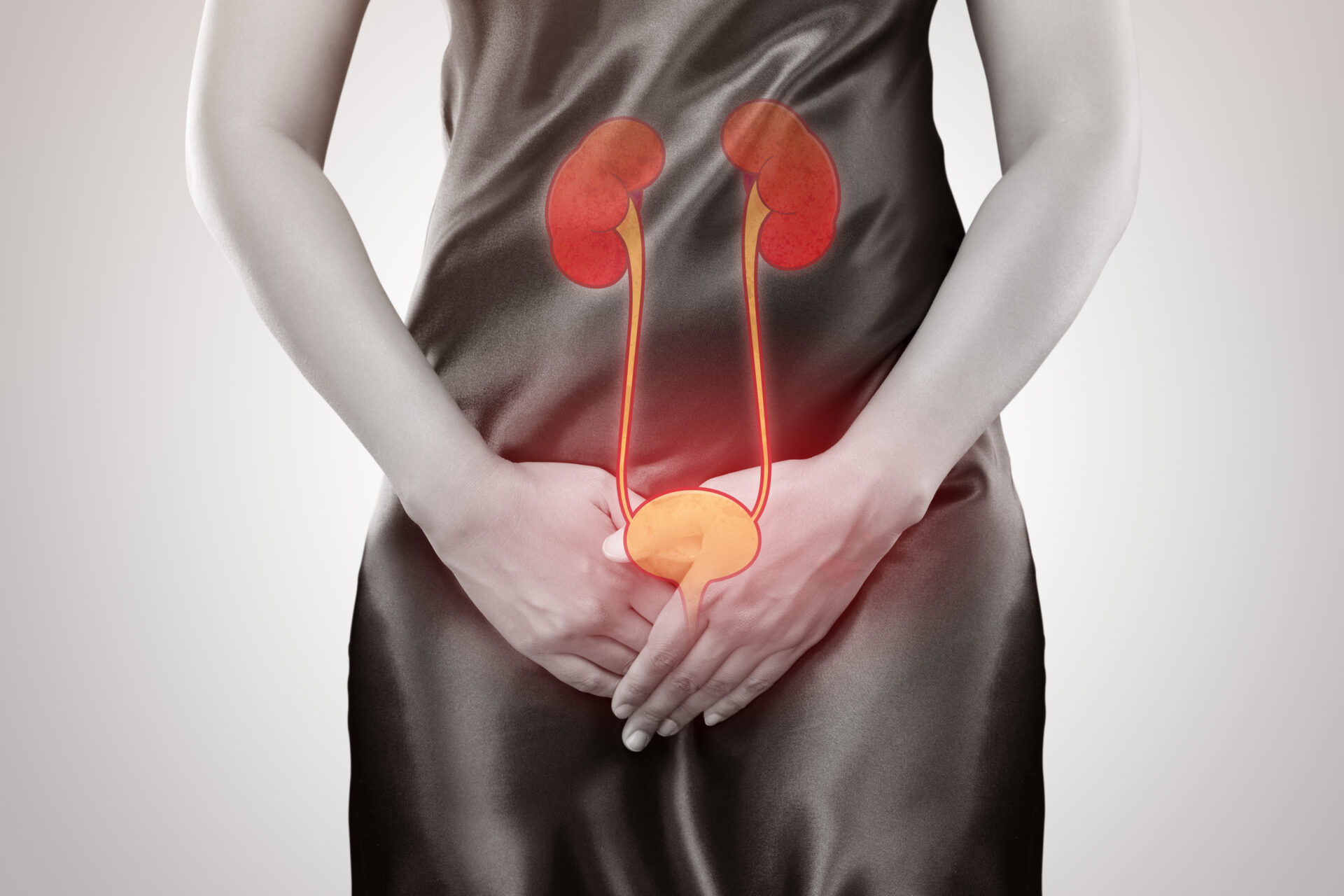
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a broad term encompassing infections in any part of the urinary tract, including the kidneys, bladder, and urethra. It specifically refers to the presence of microbial pathogens in the urinary tract. 1,2 The urinary tract is categorised into the upper (kidney and ureters) and lower tract (bladder and urethra). 2
Women are considerably more prone to developing UTIs compared to males. Approximately one in three women will have experienced at least one episode of UTI necessitating antimicrobial therapy by the age of 24 years. 1
UTI Susceptibility: Who Is the Most at Risk?
There is a certain subset of people who are at a high risk of developing UTI. 1,2
HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus.
Exploring the Commonality of UTIs: Key Contributing Factors
UTIs are more prevalent in females due to the shorter and closer proximity of their urethras to the rectum, facilitating easier entry of bacteria into the urinary tract. 3,4
Here are other factors that increase the risk of acquiring UTI: 2,3
Recognising the Signs: Common UTI Symptoms
Here are several noteworthy symptoms of a UTI that require attention. 2,4
UTI-Free Living: Incorporating Prevention Into Your Routine
The subsequent measures can be adopted to prevent UTI: 3,4
Navigating UTI Care: Treatment Strategies
Most UTIs resolve on their own, patients often seek treatment for symptom relief. The goal of the treatment is to prevent the infection from spreading to the kidneys or progressing into an upper tract disease, which can damage delicate kidney structures and eventually lead to hypertension. 4
Mild UTI generally responds well to oral antibiotics, such as fosfomycin trometamol, nitrofurantoin macrocrystal, amoxicillin/clavulanate, ciprofloxacin, cephalosporin, and co-trimoxazole. 2,5,6
Most UTIs can be treated at home by taking antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare professional. However, certain cases may necessitate hospital treatment. 3
References
- Foxman B. Epidemiology of urinary tract infections: Incidence, morbidity, and economic costs. Disease-a-Month. 2003;49:53–70.
- Tan CW, Chlebicki MP. Urinary tract infections in adults. Singapore Med J. 2016;57:485–490.
- CDC. Suffering from a urinary tract infection? Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/uti.html. Accessed on: 17 November 2023.
- Bono MJ, Leslie SW, Reygaert WC. Urinary Tract Infection. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470195/. Accessed on: 8 November 2023.
- Chu CM, Lowder JL. Diagnosis and treatment of urinary tract infections across age groups. AJOG. 2018;219:40–51.
- Koh SWC, Ng TSM, Loh VWK, et al. Antibiotic treatment failure of uncomplicated urinary tract infections in primary care. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2023;12:73.
About Frontier Healthcare Group
Frontier Healthcare (as part of the Qualitas Primary Care Division) runs 18 GP clinics, 2 Family Medicine Clinics (Clementi and MacPherson) and has 37 affiliated GP clinics under its Frontier Primary Care Network Program. Frontier Healthcare supports national schemes such as the Community Health Assist Scheme (Pioneer, Merdeka, CHAS Green, CHAS Orange, CHAS Blue), Baby Bonus, Healthier SG, MBS@Gov etc, as well as partnerships with major Insurers, Corporates and TPA partners to bring quality and affordable healthcare closer to the community.