Health Resources
- Home
- Health Resources
- The Art of Health Screening: A Layman’s Guide to Evidence-Based Care
The Art of Health Screening: A Layman’s Guide to Evidence-Based Care

Taking care of our health is a lifelong endeavor, and one of the key aspects of maintaining good health is regular health screening. Health screening allows us to detect potential health issues early on, providing us with a better chance of successful treatment and prevention. In this lighthearted article, we will explore the world of health screening, debunk some myths, and provide evidence-based guidelines for a layman’s approach to maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Understanding Health Screening:
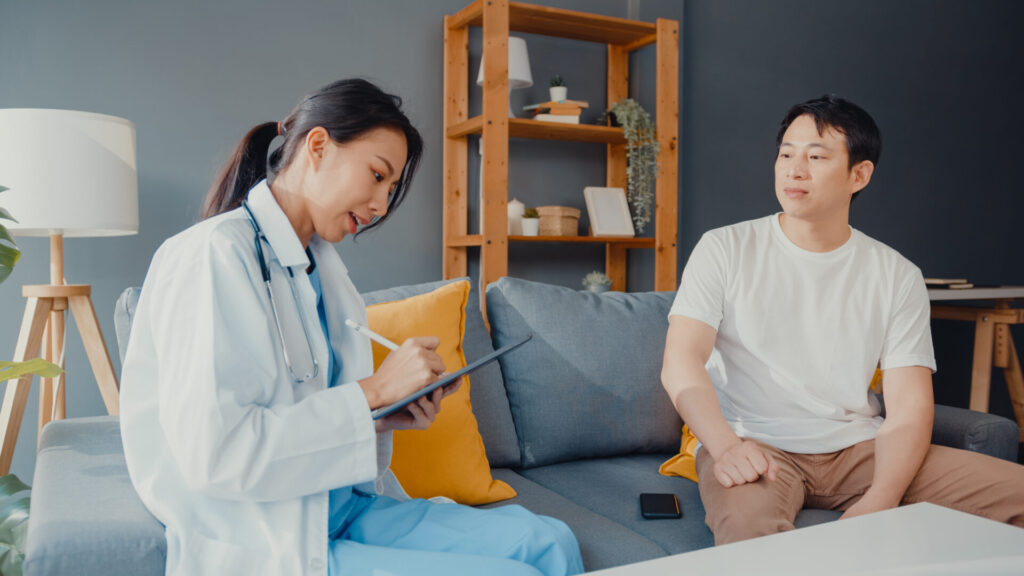
Health screening involves a series of tests and examinations that aim to identify diseases or risk factors in individuals before they show symptoms. It plays a crucial role in preventive healthcare, enabling healthcare providers to intervene early and improve outcomes. Screening tests may vary based on age, gender, and individual risk factors, and it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate screening tests for you.

The Benefits of Health Screening:
Regular health screening offers several benefits, such as:
- Early Detection: Many diseases, such as cancer and heart disease, are more manageable when detected early. Screening tests can detect abnormalities before symptoms manifest, giving you a head start on treatment (CDC, 2021).
2. Preventive Measures: Screening identifies risk factors that can be modified through lifestyle changes or medical interventions. For example, high cholesterol can be managed with dietary changes and medication (NHLBI, 2020).
3. Peace of Mind: Negative screening results can provide reassurance and peace of mind, allowing you to focus on your overall well-being (WHO, 2021).
Commonly Recommended Screening Tests:
The specific screening tests recommended for individuals may vary based on factors such as age, sex, and medical history. Here are some commonly recommended tests:
- Blood Pressure Measurement: High blood pressure is a significant risk factor for heart disease and stroke. Regular blood pressure checks can help identify hypertension early (AHA, 2021).
2. Cholesterol Screening: High cholesterol levels can increase the risk of heart disease. Lipid profiles help assess cholesterol levels and determine if lifestyle modifications or medication are needed (NHLBI, 2020).
3. Cancer Screenings: Regular screenings for breast, cervical, colorectal, and prostate cancers are recommended for certain age groups. Mammograms, Pap tests, colonoscopies, and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests are examples of common cancer screening tests (ACS, 2021).
4. Blood Glucose Testing: Diabetes is a growing health concern worldwide. Regular blood glucose testing can help identify individuals at risk or those with undiagnosed diabetes (ADA, 2021).
Debunking Myths:
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| “Screening tests always detect diseases with 100% accuracy.” | No screening test is perfect, and false positives and false negatives can occur. However, screening tests significantly improve the chances of detecting diseases early (USPSTF, 2019). |
| “If I feel fine, I don’t need screening.” | Many diseases are silent and do not exhibit symptoms until later stages. Regular screening can catch these diseases before symptoms develop (CDC, 2021). |
| “Screening tests are painful and uncomfortable.” | While some tests may cause slight discomfort, most screenings are minimally invasive and well-tolerated. The benefits of early detection outweigh temporary discomfort (NHS, 2021). |
Ensuring Evidence-Based Care: When it comes to health screening, it’s crucial to rely on evidence-based guidelines. These guidelines are developed by expert panels and organizations after extensive research and review of scientific literature. Always consult with your healthcare provider to determine which screenings are appropriate for your individual needs.
Health screening is an essential part of maintaining overall well-being. By taking a proactive approach and embracing evidence-based guidelines, you can increase your chances of early disease detection, preventive measures, and peace of mind. Remember, your healthcare provider is the best resource to guide you in determining the appropriate screening tests for your unique circumstances.
References:
- American Cancer Society (2021). Cancer Screening Guidelines. Retrieved from www.cancer.org
- American Diabetes Association (2021). Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes. Retrieved from www.diabetes.org
- American Heart Association (2021). Understanding Blood Pressure Readings. Retrieved from www.heart.org
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (2021). The Value of Prevention. Retrieved from www.cdc.gov
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) (2020). High Cholesterol. Retrieved from www.nhlbi.nih.gov
- National Health Service (NHS) (2021). Screening: Getting Tested for Cancer. Retrieved from www.nhs.uk
- U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) (2019). Understanding Task Force Recommendations: Screening. Retrieved from www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org
- World Health Organization (WHO) (2021). Noncommunicable Diseases. Retrieved from www.who.int
Author

Dr Leong Hon Loong
MBBS, MRCEM, GDip (Fam Med), GDip (Geri Med), GDip (Occ Med)
Dr Leong is a Family Physician at Frontier Healthcare with a special interest in Emergency Medicine, Geriatric Medicine and Occupational Medicine. He currently practices at Admiralty and Ang Mo Kio.