Protect Yourself From Pneumococcal Disease With Vaccination
Understanding Pneumococcal Disease
Streptococcus pneumoniae, also known as the pneumococcus bacteria, causes pneumococcal disease1,2
.
The infection usually starts at the nasopharynx region and spreads to the lower respiratory tract causing pneumonia, to the sinuses area causing sinusitis, or to the middle ear causing otitis media (ear infection)1,3.
The average yearly hospitalisation rate for pneumococcal disease from the year 2000 to 2008 in Singapore was recorded to be 9 in every 100,000 persons4.
The National Immunisation Programme in Singapore recommends pneumococcal vaccination at infancy as early as 3 months of age to prevent the spread of this disease5.
Types of Pneumococcal Vaccines
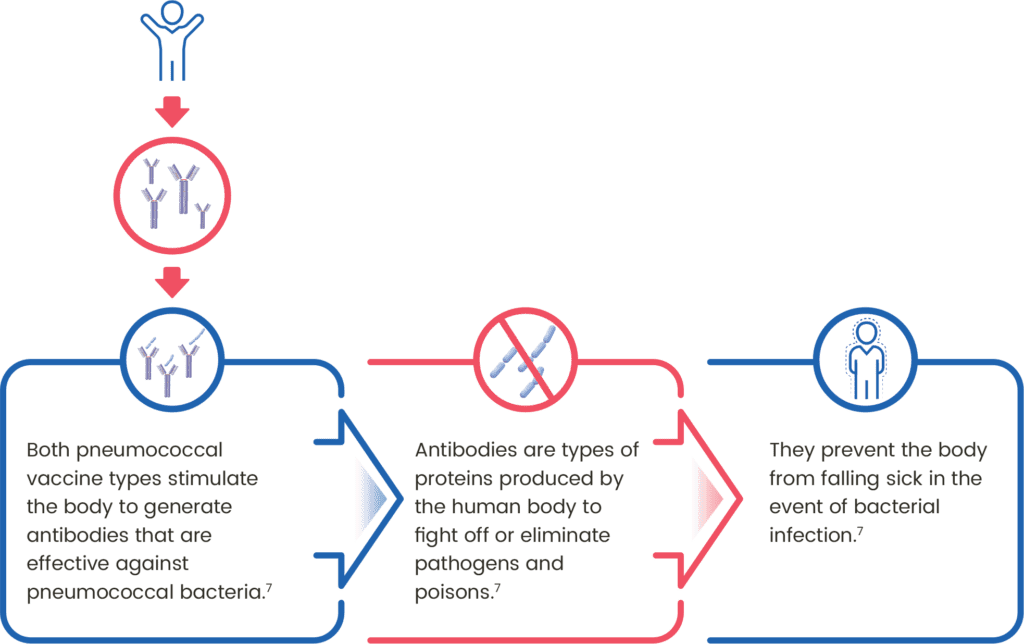
Two types of pneumococcal vaccines help to provide heightened immunisation and protection against the Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria2,6.
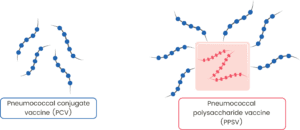
Vaccines that protect against pneumococcal disease are made from a substance called polysaccharide that comes from the bacteria that causes the disease, which is S. pneumoniae. These vaccines are called pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV) or pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV)7.
Specifically, PCV13 safeguards against the 13 prevalent strains of pneumococcal bacteria that are responsible for pneumococcal disease, whereas PPSV23 shields against 23 strains2.
Image adapted from: Walkowski et al. (2021)7
How do these vaccines work?
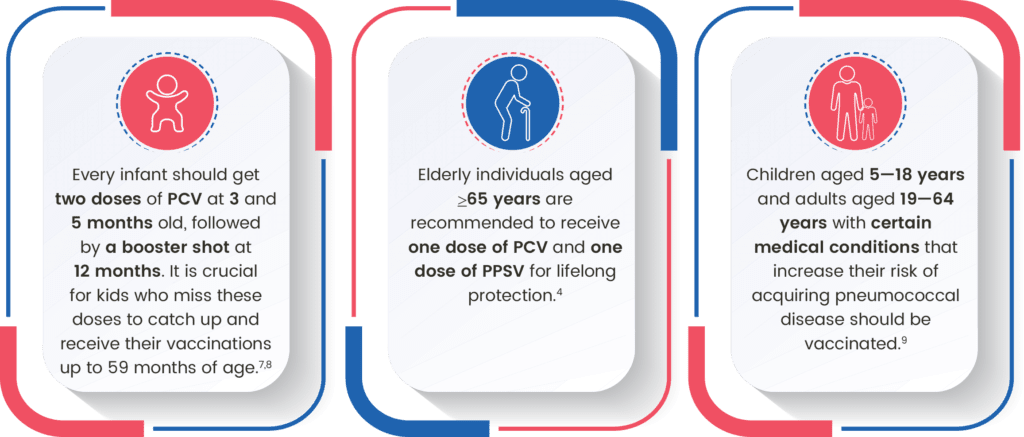
Who Should Get Vaccinated?
Individuals with the below-mentioned criteria are recommended to receive vaccination:2,5,8-11
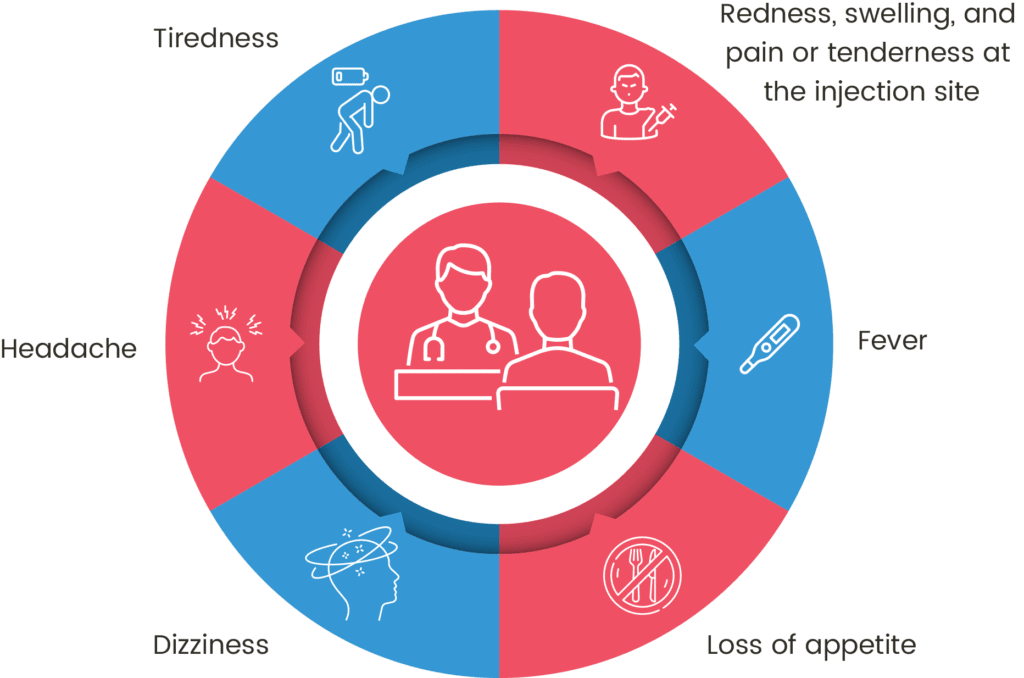
The Possible Side Effects of Vaccination
Pneumococcal vaccination is generally safe on most occasions; however, like all other vaccines, it can cause several side effects, both mild and severe ones9-11.
Contact your healthcare professional if symptoms worsen9.
Typically, side effects caused by vaccines tend to disappear on their own within 2–3 days. If pain and fever persist, paracetamol can be taken to alleviate these symptoms2
.
References
1. Dockrell DH, Whyte MKB, Mitchell TJ. Pneumococcal pneumonia. Chest. 2012;142:482–491.
2. Pneumococcal Vaccine. HealthHub.Sg. Available at: https://www.healthhub.sg/a-z/medications/375/Pneumococcal-Vaccine. Accessed on: 5 April 2023.
3. Henriques-Normark B, Tuomanen EI. The pneumococcus: Epidemiology, microbiology, and pathogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2013;3:a010215.
4. Pneumococcal Disease (Invasive) – National Centre for Infectious Diseases. Available at: https://www.ncid.sg/Health-Professionals/Diseases-and-Conditions/Pages/Pneumococcal-Disease.aspx. Accessed on: 9 March 2023.
5. National Immunisation Registry. Available at: https://www.nir.hpb.gov.sg/nirp/eservices/allAboutImmunisation. Accessed on: 9 March 2023.
6. Tereziu S, Minter DA. Pneumococcal Vaccine. StatPearls Publishing. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507794/. Accessed on: 9 March 2023.
7. Walkowski W, Bassett J, Bhalla M, et al. Intranasal vaccine delivery technology for respiratory tract disease application with a special emphasis on pneumococcal disease. Vaccines. 2021;9:589.
8. MOH | Nationally Recommended Vaccines. Available at: https://www.moh.gov.sg/resources-statistics/nationally-recommended-vaccines. Accessed on: 9 March 2023.
9. Pneumococcal Vaccination: What Everyone Should Know | CDC. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/vpd/pneumo/public/index.html. Accessed on: 9 March 2023.
10. Important information about smokers and pneumococcal disease.pdf. Available at: https://www.nfid.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/smokers.pdf. Accessed on: 9 March 2023.
11. Pneumococcal vaccine side effects. nhs.uk. Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/vaccinations/pneumococcal-vaccine-side-effects/. Accessed on: 9 March 2023.
About Frontier Healthcare Group
Frontier Healthcare (as part of the Qualitas Primary Care Division) runs 18 GP clinics, 2 Family Medicine Clinics (Clementi and MacPherson) and has 37 affiliated GP clinics under its Frontier Primary Care Network Program. Frontier Healthcare supports national schemes such as the Community Health Assist Scheme (Pioneer, Merdeka, CHAS Green, CHAS Orange, CHAS Blue), Baby Bonus, Healthier SG, MBS@Gov etc, as well as partnerships with major Insurers, Corporates and TPA partners to bring quality and affordable healthcare closer to the community.