Health Resources
- Home
- Health Resources
- Chickenpox and Varicella Vaccination
Chickenpox and Varicella Vaccination
Understanding Chickenpox: A Brief Overview
Chickenpox, caused by the varicella-zoster virus, is a common and highly contagious disease that spreads easily from person to person through direct contact or droplets from coughing or sneezing.1,2. After the initial infection, the virus can stay dormant and reactivate later as shingles, also known as herpes zoster.1,3,4
The varicella-zoster virus usually causes mild, self-limiting illness, but complications can be severe in infants and adults. Fortunately, chickenpox is preventable with the Food and Drug Administration–approved live varicella virus vaccine for individuals aged 12 months and older.3
As of August 2024, according to the weekly infectious disease bulletin from the Ministry of Health (MOH) in Singapore, the average daily number of patients seeking treatment for chickenpox is six, compared with five in 2023.5
What Are the Symptoms of Chickenpox?
Early symptoms of chickenpox may appear 1–2 days before the rash and include the following:6


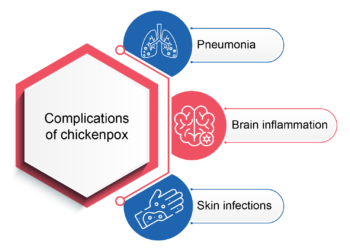
What Are the Complications of Chickenpox?
Chickenpox manifests more severely in adults than in children. The complications include7
Importance of Chickenpox Vaccination
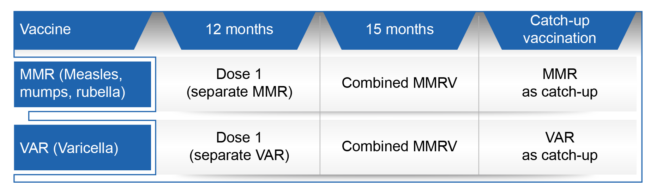
In November 2020, the National Childhood Immunisation Schedule (NCIS) added varicella-containing vaccines to reduce disease incidence and complications. The first dose, given at 12 months, can be administered with the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine. The second dose, given at 15 months, uses the combined measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella vaccine.8
Singapore NCIS: MMR + Varicella Immunisation Schedule
How Does the Chickenpox Vaccine Protect You?

The varicella vaccine is usually injected into the upper arm or the thigh region.3
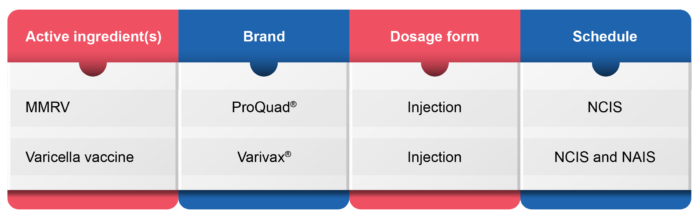
Indications and Dosage3,8,10
What Are the Adverse Effects of Varicella Vaccination?

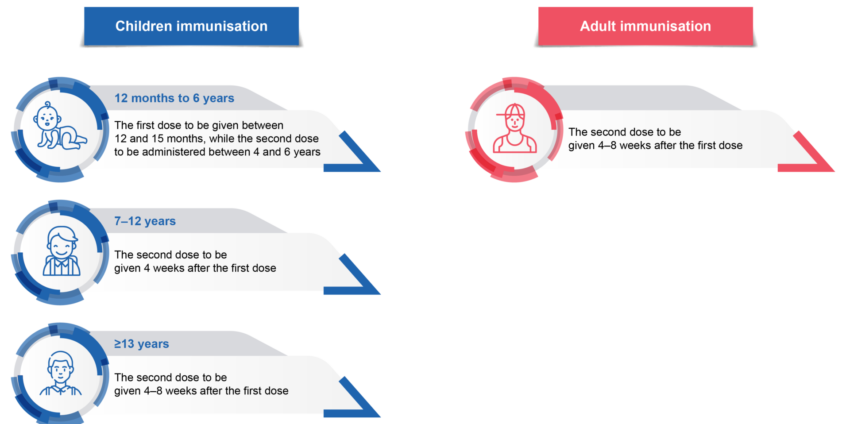
Singapore’s Recommended Vaccination Schedules

References
1. Gabutti G, Franchi M, Maniscalco L, et al. Varicella-zoster virus: Pathogenesis, incidence patterns and vaccination programs. Minerva Pediatr. 2016;68:213–225.
2. MOH | Communicable Diseases Surveillance in Singapore 2005. Available at: https://www.moh.gov.sg/resources-statistics/reports/communicable-diseases-surveillance-in-singapore-2005. Accessed on: 29 July 2024.
3. Kota V, Grella MJ. Varicella (Chickenpox) Vaccine. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441946/. Accessed on: 29 July 2024
4. Varicella (chickenpox) vaccine – What you need to know: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. Available at: https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007612.htm. Accessed on: 29 July 2024.
5. Ministry of Health Singapore: Weekly infectious disease bulletin ew33-2024.pdf. Available at: https://www.moh.gov.sg/docs/librariesprovider5/default-document-library/weekly-infectious-disease-bulletin-ew33-2024_finalf9d8184c7abf4a5b9d37992f758e9e9b.pdf?sfvrsn=1a67528c_0. Accessed on: 23 August 2024.
6. CDC. Chickenpox Symptoms and Complications. Chickenpox (Varicella). Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/chickenpox/signs-symptoms/index.html. Accessed on: 29 July 2024.
7. Ayoade F, Kumar S. Varicella-Zoster Virus (Chickenpox). In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448191/(2024. Accessed on: 20 August 2024.
8. Communicable Diseases Surveillance Singapore 2019 & 2020 Chapter 7. Overview of the Immunisation Programmes in Singapore. Available at: https://www.moh.gov.sg/docs/librariesprovider5/default-document-library/chapter-7_childhood-immunization.pdf?sfvrsn=c30e052f_0. Accessed on: 30 July 2024.
9. Department of Health. Chickenpox – immunisation. Available at: http://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/healthyliving/chickenpox-immunisation. Accessed on: 29 July 2024.
10. MOH | Nationally Recommended Vaccines. Available at: https://www.moh.gov.sg/resources-statistics/nationally-recommended-vaccines. Accessed on: 29 July 2024.
11. CDC. Chickenpox Vaccination. Chickenpox (Varicella). Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/chickenpox/vaccines/index.html. Accessed on: 29 July 2024.
12. MOH | Subsidised Vaccine List. Available at: https://www.moh.gov.sg/resources-statistics/subsidised-vaccine-list. Accessed on: 30 July 2024.