Health Resources
- Home
- Health Resources
- Pneumonia in Singapore: A Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
Pneumonia in Singapore: A Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
Pneumonia is a significant public health concern globally and a major cause of hospitalisation and mortality in Singapore. Understanding this serious respiratory infection—its causes, symptoms, and the crucial steps for treatment and prevention—is essential for safeguarding our health, especially for the most vulnerable in our community.
What is Pneumonia?
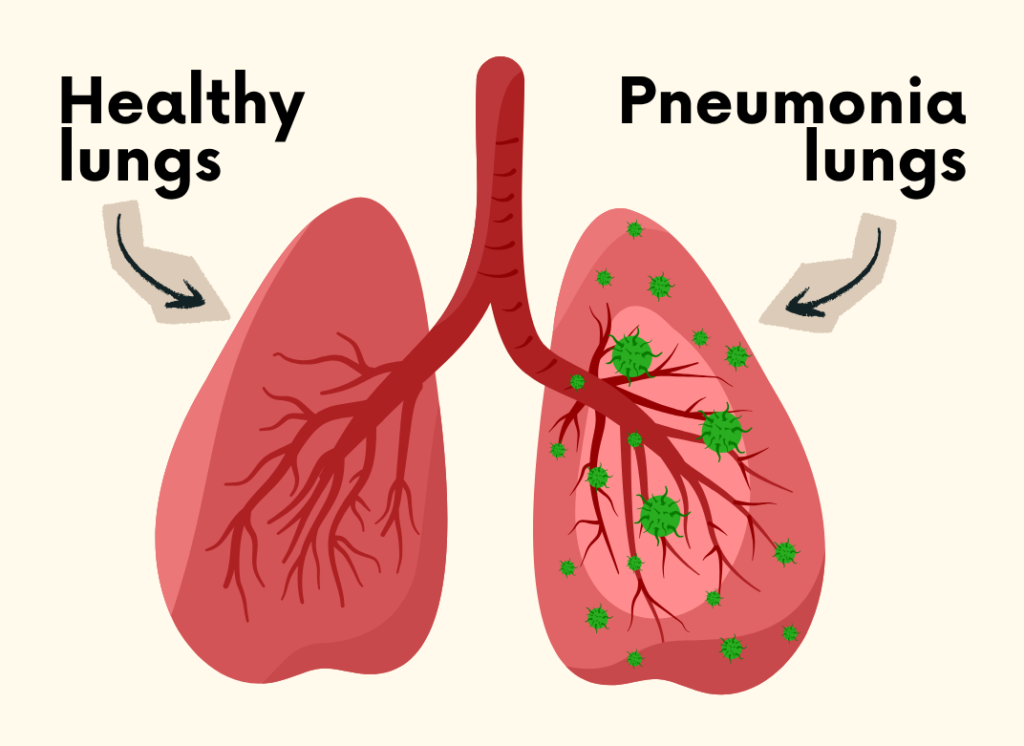
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs (alveoli) in one or both lungs. When inflamed, these air sacs may fill with fluid or pus, causing respiratory symptoms that can range from mild to life-threatening. The severity of pneumonia depends on several factors, including the type of germ causing the infection, the patient’s age, and their overall health.
The Culprits: Common Pathogens
Pneumonia can be caused by a variety of microorganisms, which are broadly classified into three groups:
- Bacteria: This is the most common cause of pneumonia in adults. The leading bacterial pathogen is Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus). Other common bacteria include Haemophilus influenzae, and atypical bacteria like Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Chlamydophila pneumoniae.
- Viruses: Viruses are another frequent cause, especially in young children and older adults. Common culprits include the influenza virus (flu), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19).
- Fungi: Fungal pneumonia is less common and typically affects individuals with weakened immune systems or chronic health problems.
Recognising the Signs: Common Symptoms
Pneumonia symptoms can develop suddenly or over several days. Key signs to watch for include:
- Cough, which may produce greenish, yellow, or even bloody mucus.
- Fever, sweating, and shaking chills.
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing.
- Sharp or stabbing chest pain that worsens with deep breathing or coughing.
- Fatigue and loss of appetite.
- Confusion or changes in mental awareness, particularly in older adults.
When It Gets Serious: Complications of Pneumonia
If not treated promptly and effectively, pneumonia can lead to severe complications:
- Bacteremia and Sepsis: The infection can spread into the bloodstream, leading to a life-threatening condition called sepsis, where widespread inflammation can cause organ failure.
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): This is a severe form of respiratory failure requiring intensive care and mechanical ventilation.
- Lung Abscesses: Pus can form in a cavity within the lung.
- Pleural Effusion: Fluid can build up in the thin space between the lung and the chest wall.
The Local Impact: Latest Mortality Rates in Singapore
In Singapore, pneumonia consistently ranks as one of the top causes of death. According to the Ministry of Health’s latest reports on principal causes of death, pneumonia is the second leading cause of death, just after cancer. It accounts for over 20% of all deaths, a figure that underscores its significant impact, especially on the nation’s aging population.
Confirming the Diagnosis
To diagnose pneumonia and determine the best course of treatment, doctors typically follow a structured approach:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A key part of the physical exam involves listening to your lungs with a stethoscope to check for abnormal sounds, such as crackling or bubbling.
- Pulse Oximetry: This non-invasive test measures the oxygen saturation level in your blood to assess how well your lungs are functioning.
- Chest X-ray: This is the most common and reliable method to confirm a pneumonia diagnosis, as it can show the location and extent of the inflammation in the lungs.
- Other investigations that may be required
- Blood Tests: A complete blood count can help determine if the body is fighting an infection (e.g., by checking for a high white blood cell count).
- Sputum Culture: A sample of mucus coughed up from the lungs can be analysed in a lab to identify the specific pathogen causing the infection, which helps in guiding antibiotic choice.
Treatment of Pneumonia: Singapore's Clinical Practice Guidelines
Treatment for pneumonia in Singapore is guided by severity and the likely causative pathogen.
- For Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP):
- Antibiotics: For bacterial pneumonia, antibiotics are the primary treatment. The choice of antibiotic depends on the patient’s age, risk factors, and local antibiotic resistance patterns. It is crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if you start to feel better.
- For Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP):
- Supportive Care: This is vital for recovery and includes:
- Rest and Hydration: Getting adequate rest and drinking plenty of fluids.
- Fever and Pain Relief: Using over-the-counter medications like paracetamol.
- Hospitalisation: Severe cases, especially among the elderly or those with other health conditions, often require hospitalisation for intravenous (IV) antibiotics, oxygen therapy, and close monitoring.
- Supportive Care: This is vital for recovery and includes:
The Best Defence: Prevention with Vaccination
Prevention remains the most effective strategy against pneumonia.
Pneumococcal vaccination is highly recommended as it protects against infections caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, the most common bacterial cause of pneumonia.
In addition to the pneumococcal vaccine, other preventive measures include:
- Getting the annual influenza vaccine
- Practising good hand hygiene
- Quitting smoking, as smoking damages the lungs’ natural defences
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle to keep your immune system strong.

References:
- HealthHub, Singapore. (2024). Pneumonia. [Online]. Available at: https://www.healthhub.sg/health-conditions/topic_pneumonia (Accessed: 12 October 2025).
- Ministry of Health, Singapore. (2025). National Adult Immunisation Schedule. [Online]. Available at: https://www.moh.gov.sg/resources-statistics/nationally-recommended-vaccinations/national-adult-immunisation-schedule (Accessed: 12 October 2025).
- Ministry of Health, Singapore. (2025). New Vaccines Against Shingles And Pneumococcal Disease Added To National Adult Immunisation Schedule. [Online]. Available at: https://www.moh.gov.sg/news-highlights/details/new-vaccines-against-shingles-and-pneumococcal-disease-added-to-national-adult-immunisation-schedule (Accessed: 12 October 2025).
- Ministry of Health, Singapore. (2024). Principal Causes of Death. [Online]. Available at: https://www.moh.gov.sg/resources-statistics/singapore-health-facts/principal-causes-of-death (Accessed: 12 October 2025).
- World Health Organization. (2023). Pneumonia. [Online]. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/pneumonia (Accessed: 12 October 2025).
Author

Dr Koh Tingyi
MB BCh BAO, MMed (Family Med)
Dr Koh is a Family Physician at Frontier Healthcare with a special interest in Chronic Disease Management, Paediatrics, Women’s Health and Care Planning . She currently practices at Clementi and Jurong West.